
NJ STAIR RAIL CODE CODE
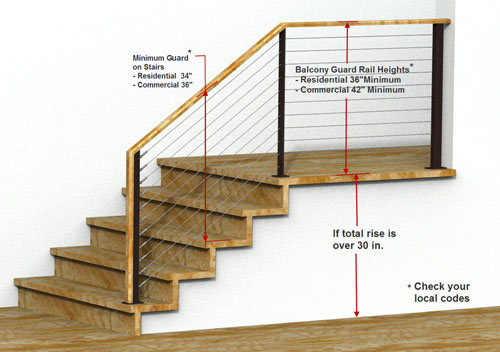
This article series provides building code specifications, sketches, photographs, and examples of stair & railing safety defects used in inspecting indoor or outdoor stair railings or handrails and related conditions for safety and proper We explain the difference between a handrail, a stair rail and a guardrail, and we provide specifications and building code specifications & sketches of proper, safe, and improper, unsafe handrails and other types of railings. Railings used on stairs, balconies, decks, ramps, walks: We have no relationship with advertisers, products, or services discussed at this website. You could compare all the ADA, OSHA and IBC stair railing height requirements here.InspectAPedia tolerates no conflicts of interest. Handrails must be on both sides of the IBC stairs, and they must comply with these additional handrail requirements. Shown below, the guards are vertical balusters, but guards can also be pieces of glass, wire, etc. Any spacing in the guards must be less than 4 inches. The guard height must be at least 42 inches high, and it is measured vertically from the leading edges of the tread nosings or from the landing surface. Guards are required along all open-sided walking surfaces of the stairway, including landings and stairs.
You can have walking surfaces with openings, but the openings cannot allow a 1/2-inch diameter sphere pass through.The slope of the walking surface cannot be greater than 1:48 in any direction.

If a wheelchair space is required for an area of refuge, the wheelchair space cannot be located in the required minimum landing dimensions or door swing.Įvery 12 feet of vertical rise, the stairway must have a landing.When the door is fully open, it cannot project more than 7 inches into the minimum dimensions of the landing.Doors opening onto a landing cannot reduce the minimum landing width to less than half.Where the stairway has a straight run, the landing does not need to be more than 48 inches deep.The width of landings must be as wide as the stairways that they serve.There must be a floor or landing at the top and bottom of each stairway.Solid risers are required for IBC stairs except for means of egress stairways as long as the opening between treads does not allow a 1/2 inch diameter sphere to pass through. The difference between the largest and smallest tread depth or riser height cannot be more than 3/8 inch. IBC stairs must have the same riser and tread dimensions throughout the stairway. If the stairs have nosings, you measure from the leading edge of the nosing to the edge of the next step’s nosing. The step height, also known as the riser height, must be no less than 4 inches and no greater than 7 inches. Riser Height and Tread Depth (IBC 1011.5) The clearance must continue past the last step for at least one stair tread depth. Stairways are required to have a headroom clearance of 80 inches from the edge of each stair nosing measured vertically up to the ceiling. Read More: Differences in IBC and OSHA Requirements Headroom (IBC 1011.3) You must calculate the IBC stair width for multi-story stairways versus single-story stairways. However, the very minimum width between handrails is 44 inches. In short, the width is calculated by multiplying the occupant load served by such stairs by a factor of 0.3 inch per occupant. The number of occupants on each floor will determine the required width of the stairs. The International Building Code (IBC) has many requirements for stairways, and you must also meet the required number of means of egress and areas of refuge for wheelchairs.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
